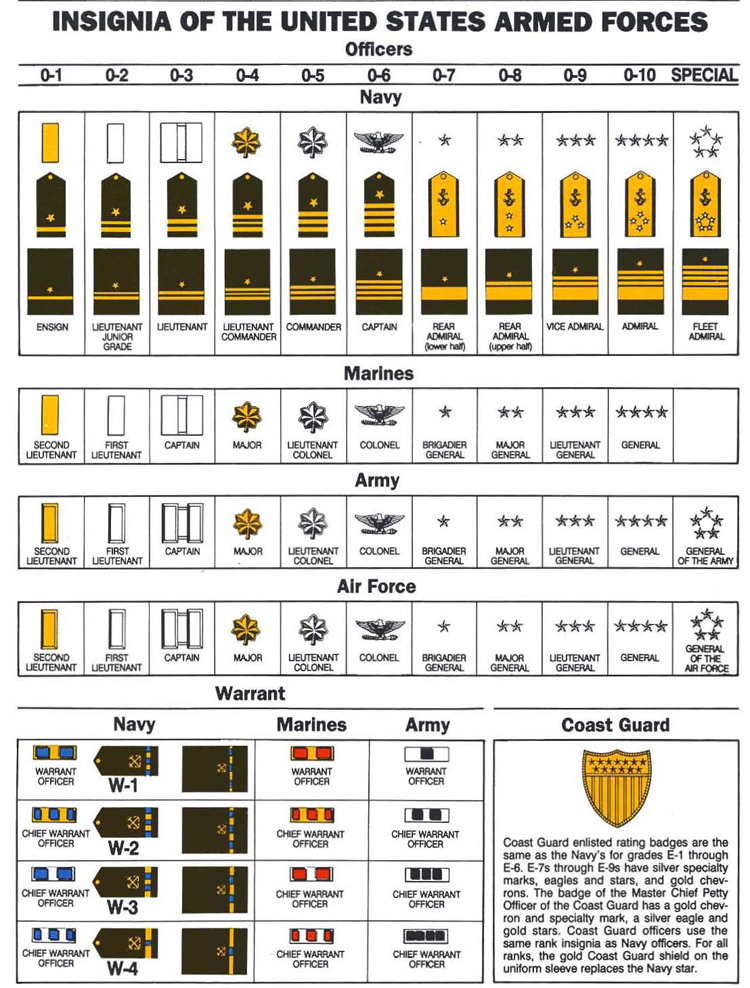
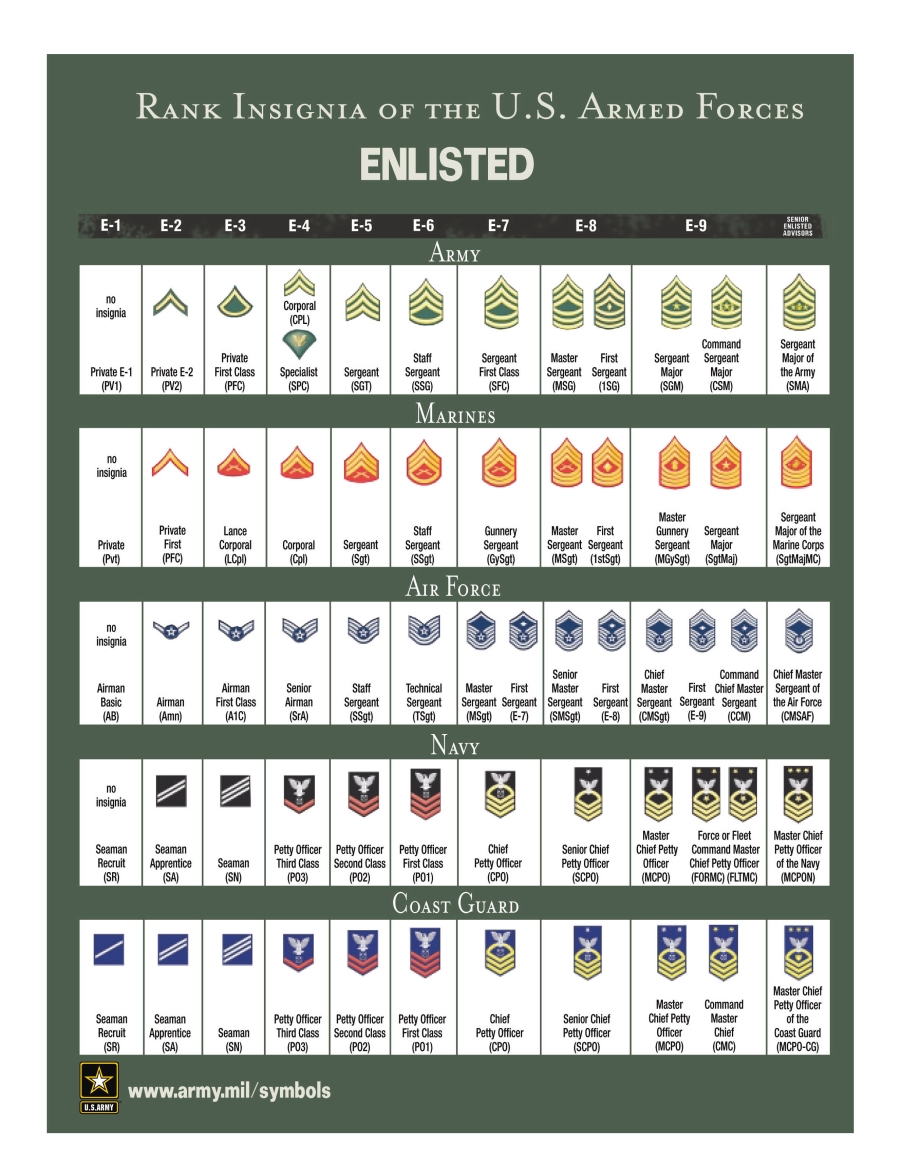
US Military Pay Grade
For the U. S. military, basic pay is established by grade and years of service. Longevity pay raises are based on your creditable cumulative service in any and all branches of the armed forces* (there are statutory periods when service in a particular component may not be counted). Pay grade or rank is computed from the official date of advancement - you will not receive the pay of an advanced rank when you are in a "frocked" status.
For most members who enter and serve on active duty, without a break in service, the basic pay date is the date they enter active or inactive service. If, however, there is a break in service, the time between periods of service usually is not included. Your personnel office is responsible for providing the basic pay date, total active federal military service date, total commissioned federal military service date, and a variety of other dates, depending on the nature of the individual member's service.Military basic pay indicated in the charts are monthly amounts that are distributed on the 1st and 15th day of the month. If the 1st or 15th fall on a weekend or national holiday payment will be made the working day prior. The charts are good for active and reserve components of the Navy, Marines, Army, Air Force, Coast Guard and National Guard.
All pay grades, $150.00. Hazardous duty includes duty involving; parachute jumping as an essential part of military duty, frequent and regular participation in flight operation on the flight deck of an aircraft carrier or ship other than aircraft carrier from which aircraft are launched, the demolition of explosives as a primary duty, including training for such duty - duty inside a high or low-pressure chamber - duty as a human acceleration or deceleration experimental subject, duty as a human test subject in thermal stress experiments, duty involving the servicing of aircraft or missiles with highly toxic fuels or propellants, fumigation tasks utilizing highly toxic pesticides, laboratory work utilizing live dangerous viruses or bacteria, handling of chemical munitions, maritime visit, board, search and seizure operations and duty involving use of ski-equipped aircraft on the ground in Antarctica or on the Arctic ice-pack.
All pay grades, $225.00. For Imminent Danger Pay (IDP), Sailors will receive $7.50 for each day on duty in an IDP-eligible area up to the maximum monthly rate of $225. For Hostile Fire Pay (HFP), Sailors who are exposed to hostile fire or a hostile mine explosion event are eligible to receive non-prorated HFP at the full monthly amount of $225. Members may not receive both IDP and HFP in the same month.
45,000, $60,000, $75,000 or $90,000 cap depending on rating/classification and time in service. SRB is calculated by multiplying your basic pay (times) number of SRB eligible months reenlisting for (divided by 12) then multiplied by the SRB award level for your zone. Zone A is 2 to 6 years, Zone B is 6 to 10 years and Zone C is 10 to 14 years of active service. For the latest eligible SRB Zone award levels and caps
To encourage service in the nuclear enlisted community's most challenging billets and to provide incentives that promote career longevity, ESRP uses the critical skills retention bonus (CSRB) legislative authority to provide a retention incentive for members assigned to Nuclear Navy Enlisted Classification (NEC) codes. Individual ESRP reenlistment contracts are limited to $100k.